So, you have your feeds all optimized to the brim, but you also want to ramp up the campaigns and bidding strategies? Are you a small or medium company looking to make sense of all the information that is out there on Google Shopping campaigns?
Here, we are going to look at five tips to help you ramp up your shopping campaigns and your bidding strategies for Google Shopping.
1. Use RLSAs to Supercharge your Shopping Campaigns
Remarketing lists for search ads can increase your CTR & CVR by 400%, by allowing merchants to target past website visitors and adjust their bidding strategies based on the past actions.
Remarketing lists can be split out to segment people who have visited some areas of your site, but not others. E.g. you may want to show your PLAs for running shoes to people who have previously viewed running shoes on your site but not reached the checkout.
The image below shows how this looks in Audience definition in Analytics.
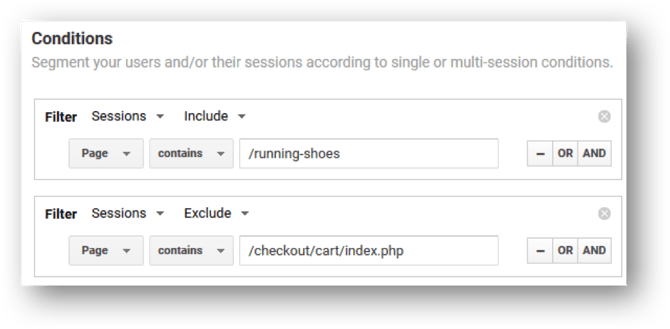
Other types of segments you can use for retargeting are:
- visitors that viewed a promotion page
- visitors that viewed a product detail page or a category page
- shoppers that started, completed or abandoned the checkout process
- shoppers that added or removed products from the shopping cart
Netpeak used Remarketing Lists for Shopping to achieve an ROI of 239.7%. Although the case study is more than one year old, the methodology and insights discussed in this case-study prove the point that there's value in remarketing.
2. Use Customer Match to bring back old Customers
In the same vein as RLSAs, using customer match for Google Shopping can significantly improve the response your PLAs receive.
Customer match allows advertisers to use their email address lists to let Google find people considered ‘similar’. This helps you find more specific internet users to show your ads to which should help to improve conversion rate.
CPC strategy found that as RLSAs were cookie-based they were not as reliable as many customers could choose to block or avoid. On the other hand, Customer Match was considered more reliable across all devices as it was based on email addresses and logins.
Types of customers that can be targeted with Customer Match include:
- Upsell to recent purchasers- customers who already know your brand and have recently purchased from you.
- Cross-sell to past customers- Past customers convert better than new ones.
- Target frequent re-purchasers -Buyers from your loyalty program should be rewarded.
- Offline Buyers -the purchasing behaviors have changed massively in the past few years and the biggest change is that customers are now having multiple online interactions with a brand before making the ultimate purchase decision.
- In-app customers -according to Criteo's latest study on thestate of the mobile commerce the conversion rate of mobile browsers versus mobile apps is quite striking: 39% conversion rate versus 90% conversion rate.
Related: Start Selling on Criteo - User Guide
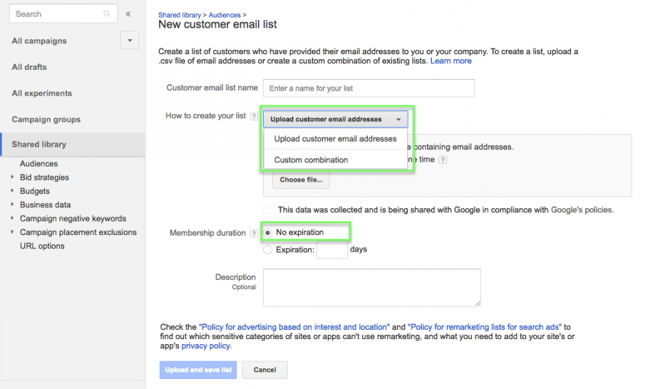
If you want to know more on Customer Match on Google Shopping we've covered at length the ins and outs of this functionality.

3. Be aware of bidding too much
It seems like an obvious point as nobody ever wants to have to bid more than they have to. However, when it comes to Google Shopping, there is such thing as ‘overbidding’.
This differs to other campaign types (such as search or display) where increasing the bid amount will not always increase the quantity of conversions.
In fact, there is typically a point in which the CPC can be raised and conversions will grow with the increase. At a certain point however, the conversions stop increasing with the CPCs. This graph below highlights this:
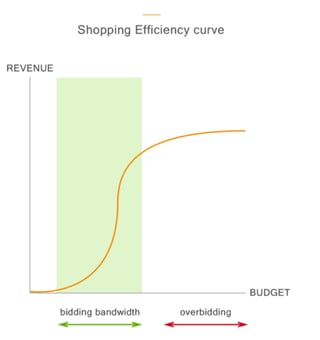
Source: Search Engine Land
Search Engine Land also looked at bidding strategies to solve some of the major issues retailers were experiencing with Google Shopping.
Their solution was ‘Query Level Bidding’ which has the primary goal of creating a Google Shopping strategy that allows you to quickly and easily bid separately depending upon the search query.
Find out more about the strategy and how you can use it here.
4. Try SKU Level Bidding
This is one for those who want to compete against big players and are not afraid to work for it. This is the most granular way to bid on Shopping which gives you full control.
The chances are you’ve split out your product groups by one of the following attributes:
- Brand
- Category
- Custom Level
- Product type
However, in each of these groups, the chances are there will be one or two products that dominate over the others. To get better control over this you can opt to bid at SKU level.
As you can imagine, setting this up and managing it accurately can take a little while but the payoff can be worth it when you are able to optimise and bid towards conversions by each specific product.
For further information Shopify talks at length about bidding options here: Bidding - The Ultimate X Factor.
5. Consider Decreasing Prices
We hear you; this isn’t a race to the bottom and the last thing you want is to make cuts in your profit margins. However, this can be worthwhile. Instead of increasing CPCs, you could decrease item costs to undercut your competitors.
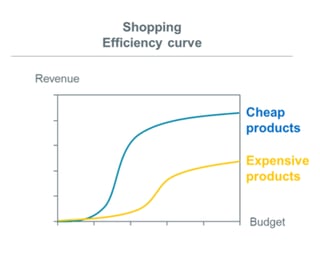
Google’s algorithm does not factor in product prices in their PLA positioning. However, it takes into account expected click-through-rate and learns about users preferences. Typically people searching will favor cheaper items, which within Google’s algorithm, looks positive.
Andreas Reiffen explains this in detail:
In an effort to make Google Shopping more appealing to online shoppers, Google seems to have what we call a “low-price bias.” That means that given the choice between two products, Google will almost always choose to show the cheaper of the two, even if the more expensive product has a higher bid. In fact, if your products are too expensive, Google may refuse to show them at all.
According to Google, their algorithm doesn’t favor cheaper products. Rather, they apply a machine learning algorithm which reacts to what users like or dislike. In this case, users apparently dislike high prices, and therefore, the algorithm chooses lower-priced products. Either way, the bottom line is the same: price matters.
This is a brief introduction to bidding ideas and tips. The bidding strategy on Google Shopping has far more to be written. However, applying these small changes to your campaign will save you money and increase the overall performance of the campaigns.
Read more about How to Improve Your Google Shopping Ads:
- Leveraging Free Shopping Ads - Step by Step Guide
- 7 Tips for Google Shopping Feed Optimization [EXPERT Level]
- 10 Easy Tricks to Optimize Your Shopping Campaigns
- 8 Tried & Tested Tactics to Optimize Your Google Shopping Titles